Penile Implant (Prosthesis) Surgery represents a safe and effective means of treating men with ED. Penile prosthesis has the highest satisfaction rates of all treatment options for erectile dysfunction. Patients who attempt but dislike or fail to achieve satisfactory results with pills, vacuum devices, suppositories or injections are counseled about penile implant surgery.
Penile prostheses can be divided into two main categories, malleable (also known as non-hydraulic or semi-rigid) and inflatable (hydraulic). At our Sexual Medicine Program at Weill Cornell Medicine, 3-piece inflatable penile prostheses are the most commonly implanted. Three-piece inflatable implants have paired cylinders, a small scrotal pump, and a large-volume fluid reservoir (which is placed behind the abdominal wall muscles).
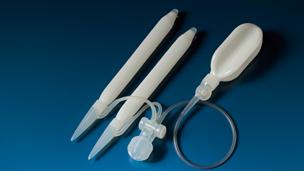
Coloplast penile implant
Prior to surgery, it is important that all patients receive appropriate education concerning the operative procedure and its associated risks and benefits. We also insist on all patients reading device literature and viewing a device video prior to committing to the procedure. Ensuring that the patient has realistic expectations prior to proceeding with implant surgery is essential to ensuring high postoperative satisfaction profiles. Patients are advised that the prosthesis will allow them to achieve a rigid erection on demand and will have no effect on their libido and will not lengthen their penis. Patients are also informed of infection rates (1-3%) and rates of re-operation 2nd to device malfunction (15% with in 8 years).
Penile implants offer the patient a very high level of satisfaction of their spontaneity, consistency, and rigidity.
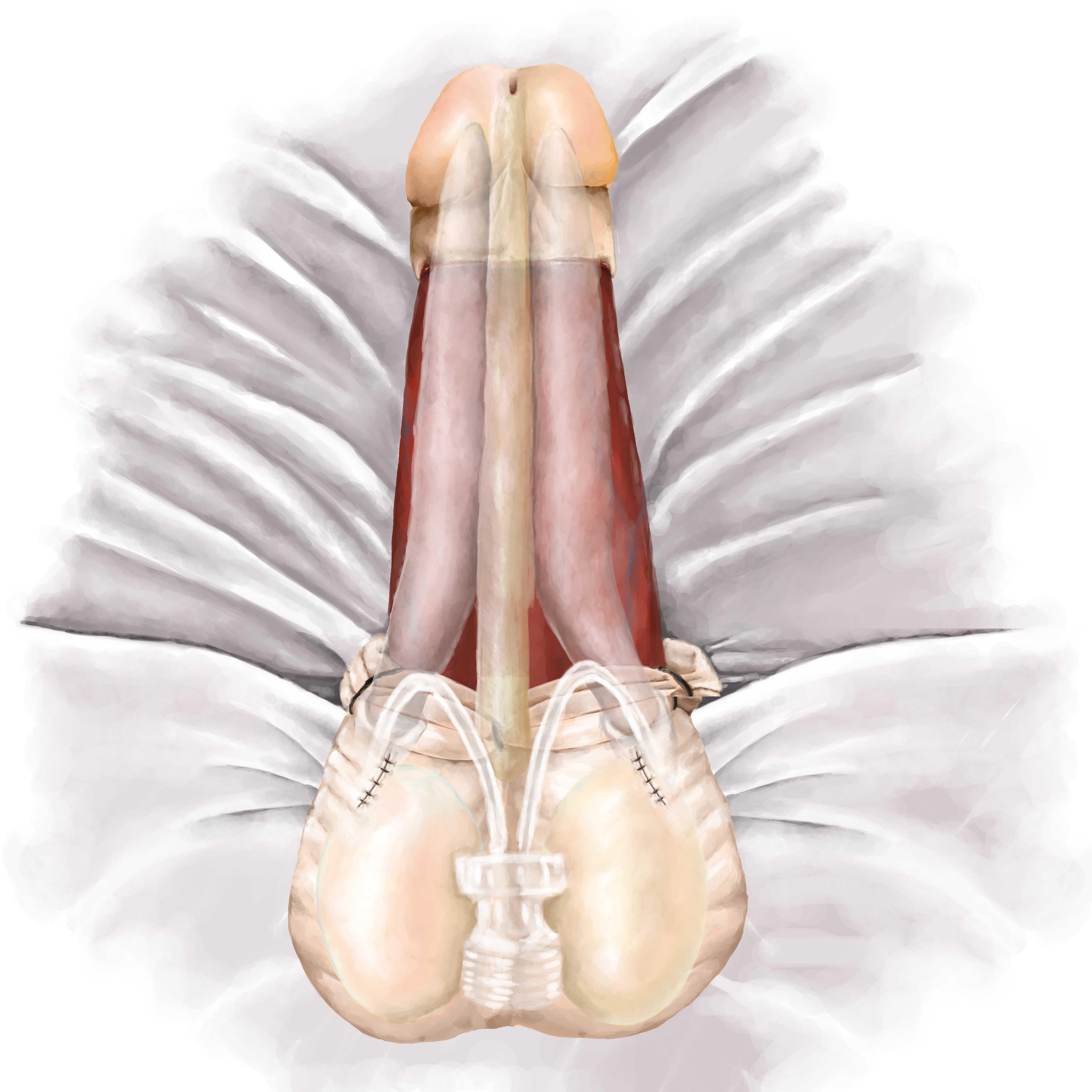
Prosthesis Selection
Prostheses can be divided into two main categories, malleable (also known as non-hydraulic or semi-rigid) and inflatable (also referred to as hydraulic). The latter can be subdivided into 2-piece and 3-piece devices depending upon the location of the fluid used for inflation.
Malleable devices have an outer shell with a central core of metal or plastic. These prostheses are paired solid devices implanted in the erectile bodies that produce constant penile rigidity. The primary advantage of these devices is their ease of implantation while the disadvantages include a constantly rigid penis that resembles neither normal erection nor flaccidity, difficulty with concealment, and an increased risk for device erosion.
Complications
Post-operative complications of penile implant surgery are not common and include but are not limited to implant infection, component failure, device erosion, device migration, sizing problems, and auto-inflation. Infection occurs in approximately 2-3% of primary (first time) implant surgeries. Infection and subsequent device removal may result in penile scaring and loss of penile length, which may lead to the inability to perform any further implant surgery. Following implantation, the time frame for the presentation of infection will vary depending on the bacteria involved. Infections with more virulent and aggressive bacteria will usually present within the first few days to weeks after surgery (fever, pain, and swelling), but low-grade infection may not present for a year after surgery. When infection of the prosthesis is diagnosed the standard treatment is the removal of the entire prosthesis and re-implantation of another device several months later. In an effort to prevent penile length loss and a difficult re-implantation procedure, prosthesis salvage has proven effective.
Satisfaction
Patient satisfaction is of utmost importance in penile implantation. Patient satisfaction is a complicated issue and is related to factors as diverse as degree of postoperative pain/swelling, postoperative complications, concealability, cosmetic outcome, implant function, ease of use and partner acceptance. It is clear that when patients are counselled appropriately, penile prosthesis implantation has the highest satisfaction rates of all treatment options for erectile dysfunction according to published reports. In one study 89% of the men and 70% of their partners were satisfied. Pain, appearance, and the need for repeat operation were factors resulting in decreased satisfaction. In another study 85% of the men and 76% of their partners were satisfied. In a study comparing penile prosthesis implantation with penile injection therapy, with similar follow-up, 70% of penile prosthesis recipients reported having sex on a regular basis, whereas only 41% of penile injection patients were still sexually active.
In a prospectively conducted study of patient satisfaction following penile prosthesis surgery, physicians at our Department of Sexual Medicine evaluated patients undergoing first-time penile prosthesis surgery. Patients completed the satisfaction questionnaires preoperatively and at 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively. Postoperative satisfaction scores increased as time passed with these scores being highest (greatest satisfaction) between 6 and 12 months after surgery.
We believe that excellent pre-operative counseling ensures realistic expectations and excellent patient satisfaction.

