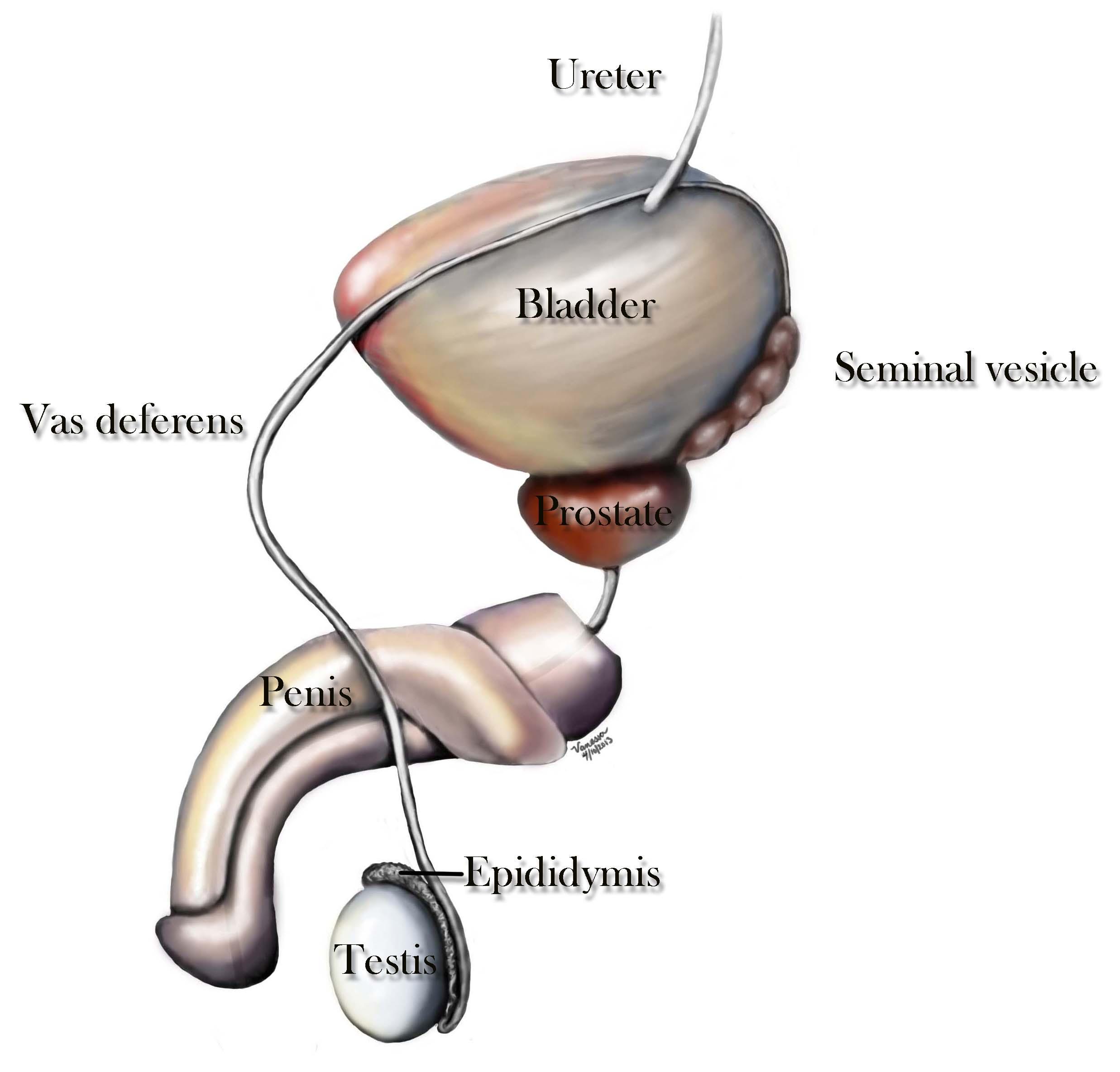
male reproductive anatomy
Vas Deferens
The vas deferens (ductus deferens) is a tubular structure derived from the mesonephric duct. Its primary function is the transport of sperm from the epididymis to the urethra, although absorptive and secretory functions have also been described (Hoffer 1976). As it arises from the cauda epididymis, the vas is tortuous for 2–3 cm. Beyond this convoluted segment, it lies posterior and parallel to the vessels of the spermatic cord, passes through the inguinal canal, and emerges in the pelvis lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels. At the internal ring, the vas diverges from the testicular vessels, coursing medial to the structures of the pelvic side wall, in order to reach the base of the prostate posteriorly. Here, the vas once again becomes tortuous and dilated (the ampulla of the vas deferens), before culminating at the ejaculatory duct.
Click here to learn about congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens.
Ejaculatory Ducts
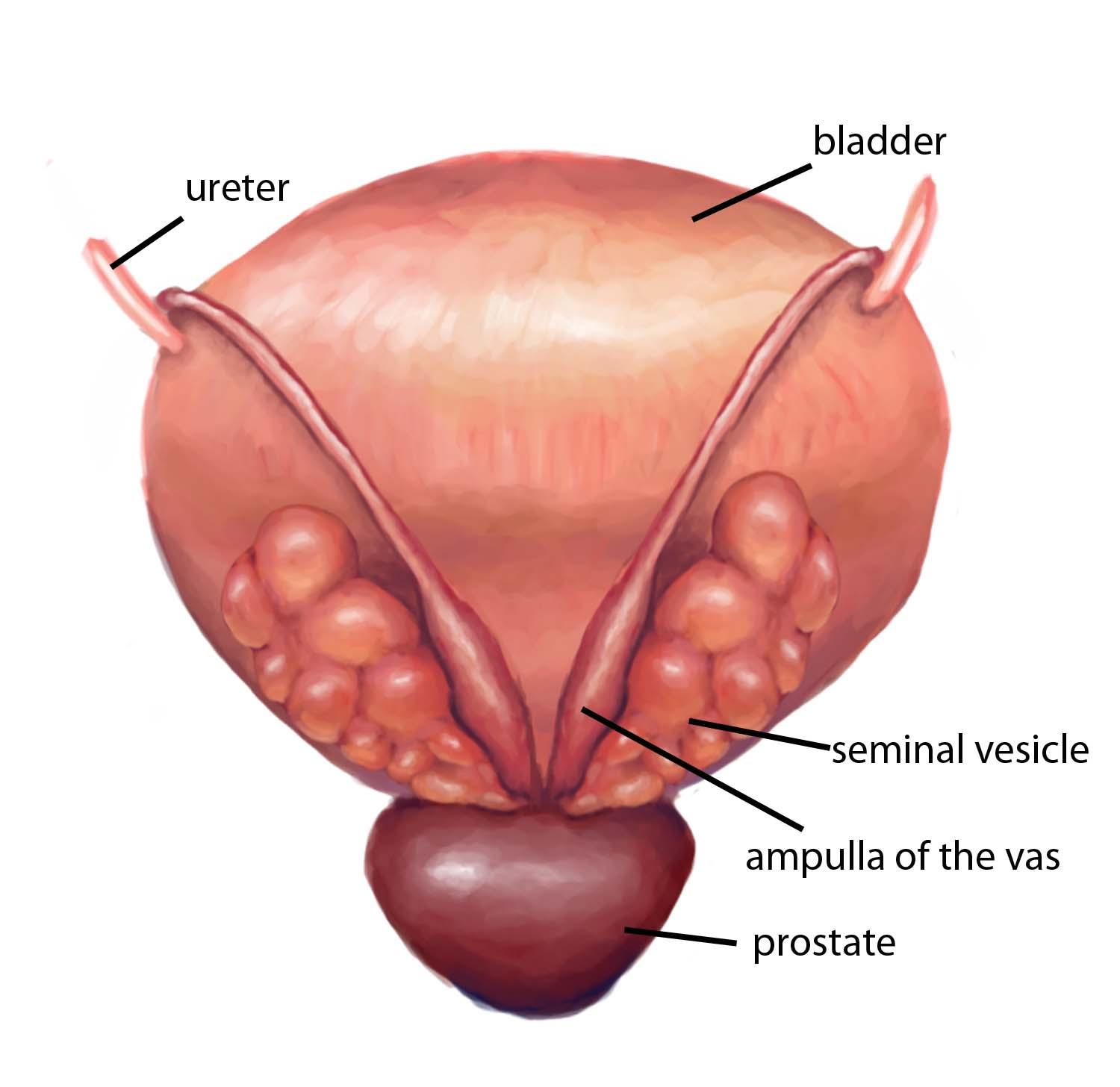
Ejaculatory Ducts
The paired ejaculatory ducts are formed from the union of the duct of the seminal vesicle with the ampulla of the vas deferens. Each is approximately 2 cm in length, and extends from the base of the prostate, between the median and lateral lobes, towards its opening on the verumontanum. The ducts diminish in size and converge towards their ends. Ejaculatory duct obstruction, though rare, can lead to oligospermia or azoospermia. Causes include congenital cysts, such as Müllerian duct cysts, or iatrogenic injury during urethral manipulation. In contrast to the walls of the vas deferens, the walls of the ejaculatory ducts are thin. They consist of an outer fibrous layer, which decreases in thickness on their entry into the prostate; a thin layer of smooth muscle fibres; and a mucosa lined by columnar epithelium. The ducts dilate during ejaculation. Normal luminal and wall dimensions of the ejaculatory duct are remarkably uniform among men; a luminal diameter of greater than 2.3 mm defines a dilated or obstructed efferent duct (Nguyen et al 1996).

